CS234 assignment 2-3
-
CS234 Assignment 2-3 solution 및 풀이2019.06.07
CS234 Assignment 2-3 solution 및 풀이

1. x를 다음과 같이 정의할 때, ^q(s, a, w) = wTx(s, a)를 만족한다면 section 2의 (1) 식과 (2) 식이 동일하다는 것을 증명하시오. [3점]
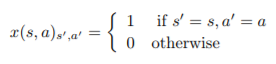
(수식이 너무 많아서 다 쓰긴 좀... 그냥 위에 있는거 대충 보고 합시다...)
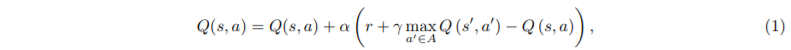
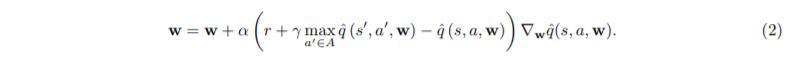
sol)
어차피 x(s, a)ₛ',ₐ' 가 0이 되면 w가 뭐든간에 ^q은 0이 되니까,
x(s, a)ₛ,ₐ = 1인 경우를 (2)번 식에 적용하면,
wₛ,ₐ= wₛ,ₐ + α(r + 𝛾max wₛ,ₐ - wₛ,ₐ)∇wₛ,ₐ wₛ,ₐ
(수식 ㅂㄷㅂㄷ;;; 대충 뭔뜻인지 이해하셨으면 좋겠는데... 그냥 ^q를 w로 바꾸고, w도 wₛ,ₐ로 바꾼 식...)
이 때, ∇wₛ,ₐ wₛ,ₐ = 1이므로 다시 정리하면
wₛ,ₐ= wₛ,ₐ + α(r + 𝛾max wₛ',ₐ' - wₛ,ₐ)
그리고 이를 다시 Q(s, a)로 정리하면 (1)번 식이 나온다.
2. qˆ(s, a, w) = wT x(s, a)이라고 할 때, value function parameter w ∈ Rⁿ에 대한 미분값을 구하고, w의 update rule을 적으시오. [3점]
sol) q^(s, a, w) = wTx(s, a)라고 했으므로,
∇w q^(s, a, w) = ∇w wTx(s, a) = x(s, a) 이다.
그리고 update rule은 아까 section 2 의 (2)번 식에 따라,
w = w + α(r + 𝛾max a0∈A qˆ(s 0 , a0 , w) − qˆ(s, a, w) )x(s, a)
가 된다. (그냥 뒤에 ∇w q^(s, a, w) 부분을 x(s,a)로 바꿈)
3. [코딩] 이제 tensorflow로 linear approximation을 구현할 것이다. 이 문제는 나머지 assignment 문제를 풀기 위한 pipeline을 작성하게 할 것이다. q2linear.py의 함수 중 다음의 함수를 구현할 것이다(q2linear.py를 읽어보라) :
• add_placeholders_op
• get_q_values_op
• add_update_target_op
• add_loss_op
• add_optimizer_op
작성한 코드를 python q2 linear.py 명령어를 사용해서 CPU에서 돌려보아라. 그러면 test environment에서 linear approximation을 실행시킬 것이다. 실행하는데 대략 1분에서 2분 정도 걸릴 것이다.
class Linear(DQN):
"""
Implement Fully Connected with Tensorflow
"""
def add_placeholders_op(self):
"""
Adds placeholders to the graph
These placeholders are used as inputs to the rest of the model and will be fed
data during training.
"""
# this information might be useful
state_shape = list(self.env.observation_space.shape)
##############################################################
"""
TODO:
Add placeholders:
Remember that we stack 4 consecutive frames together.
- self.s: batch of states, type = uint8
shape = (batch_size, img height, img width, nchannels x config.state_history)
- self.a: batch of actions, type = int32
shape = (batch_size)
- self.r: batch of rewards, type = float32
shape = (batch_size)
- self.sp: batch of next states, type = uint8
shape = (batch_size, img height, img width, nchannels x config.state_history)
- self.done_mask: batch of done, type = bool
shape = (batch_size)
- self.lr: learning rate, type = float32
(Don't change the variable names!)
HINT:
Variables from config are accessible with self.config.variable_name.
Check the use of None in the dimension for tensorflow placeholders.
You can also use the state_shape computed above.
"""
##############################################################
################YOUR CODE HERE (6-15 lines) ##################
batch_size = 5
img_height = state_shape[0]
img_width = state_shape[1]
n_channels = state_shape[2]
self.s = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.uint8,
shape=[None, img_height, img_width, n_channels * config.state_history],
name='state')
self.a = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.int32, shape=[None], name='action')
self.r = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=[None], name='reward')
self.sp = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.uint8,
shape=[None, img_height, img_width, n_channels * config.state_history],
name='next_state')
self.done_mask = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.bool, shape=[None], name='done_mask')
self.lr = tf.placeholder(dtype=tf.float32, shape=(), name='lr')
##############################################################
######################## END YOUR CODE #######################
def get_q_values_op(self, state, scope, reuse=False):
"""
Returns Q values for all actions
Args:
state: (tf tensor)
shape = (batch_size, img height, img width, nchannels x config.state_history)
scope: (string) scope name, that specifies if target network or not
reuse: (bool) reuse of variables in the scope
Returns:
out: (tf tensor) of shape = (batch_size, num_actions)
"""
# this information might be useful
num_actions = self.env.action_space.n
##############################################################
"""
TODO:
Implement a fully connected with no hidden layer (linear
approximation with bias) using tensorflow.
HINT:
- You may find the following functions useful:
- tf.layers.flatten
- tf.layers.dense
- Make sure to also specify the scope and reuse
"""
##############################################################
################ YOUR CODE HERE - 2-3 lines ##################
input = tf.layers.flatten(state, name=scope)
out = tf.layers.dense(input, num_actions, name=scope, reuse=reuse)
##############################################################
######################## END YOUR CODE #######################
return out
def add_update_target_op(self, q_scope, target_q_scope):
"""
update_target_op will be called periodically
to copy Q network weights to target Q network
Remember that in DQN, we maintain two identical Q networks with
2 different sets of weights. In tensorflow, we distinguish them
with two different scopes. If you're not familiar with the scope mechanism
in tensorflow, read the docs
https://www.tensorflow.org/programmers_guide/variable_scope
Periodically, we need to update all the weights of the Q network
and assign them with the values from the regular network.
Args:
q_scope: (string) name of the scope of variables for q
target_q_scope: (string) name of the scope of variables
for the target network
"""
##############################################################
"""
TODO:
Add an operator self.update_target_op that for each variable in
tf.GraphKeys.GLOBAL_VARIABLES that is in q_scope, assigns its
value to the corresponding variable in target_q_scope
HINT:
You may find the following functions useful:
- tf.get_collection
- tf.assign
- tf.group (the * operator can be used to unpack a list)
(be sure that you set self.update_target_op)
"""
##############################################################
################### YOUR CODE HERE - 5-10 lines #############
q = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, scope=q_scope)
target_q = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, scope=target_q_scope)
assign = [tf.assign(target_q[i], q[i]) for i in range(len(q))]
self.update_target_op = tf.group(*assign)
pass
##############################################################
######################## END YOUR CODE #######################
def add_loss_op(self, q, target_q):
"""
Sets the loss of a batch, self.loss is a scalar
Args:
q: (tf tensor) shape = (batch_size, num_actions)
target_q: (tf tensor) shape = (batch_size, num_actions)
"""
# you may need this variable
num_actions = self.env.action_space.n
##############################################################
"""
TODO:
The loss for an example is defined as:
Q_samp(s) = r if done
= r + gamma * max_a' Q_target(s', a')
loss = (Q_samp(s) - Q(s, a))^2
HINT:
- Config variables are accessible through self.config
- You can access placeholders like self.a (for actions)
self.r (rewards) or self.done_mask for instance
- You may find the following functions useful
- tf.cast
- tf.reduce_max
- tf.reduce_sum
- tf.one_hot
- tf.squared_difference
- tf.reduce_mean
"""
##############################################################
##################### YOUR CODE HERE - 4-5 lines #############
notdone = 1 - tf.cast(self.done_mask, tf.float32)
action = tf.one_hot(self.a, num_actions)
q_samp = self.r + notdone * (self.config.gamma * tf.reduce_max(target_q, axis=1))
q_s = tf.reduce_sum(q * action, axis=1)
self.loss = tf.reduce_mean((q_samp - q_s)**2)
# self.loss = tf.squared_difference(q_samp, q_s)
##############################################################
######################## END YOUR CODE #######################
def add_optimizer_op(self, scope):
"""
Set self.train_op and self.grad_norm
Args:
scope: (string) scope name, that specifies if target network or not
"""
##############################################################
"""
TODO:
1. get Adam Optimizer
2. compute grads with respect to variables in scope for self.loss
3. if self.config.grad_clip is True, then clip the grads
by norm using self.config.clip_val
4. apply the gradients and store the train op in self.train_op
(sess.run(train_op) must update the variables)
5. compute the global norm of the gradients (which are not None) and store
this scalar in self.grad_norm
HINT: you may find the following functions useful
- tf.get_collection
- optimizer.compute_gradients
- tf.clip_by_norm
- optimizer.apply_gradients
- tf.global_norm
you can access config variables by writing self.config.variable_name
"""
##############################################################
#################### YOUR CODE HERE - 8-12 lines #############
optimizer = tf.train.AdamOptimizer(learning_rate=self.lr)
variable = tf.get_collection(tf.GraphKeys.TRAINABLE_VARIABLES, scope=scope)
gradient = optimizer.compute_gradients(self.loss, variable)
if self.config.grad_clip is True:
clip_grad = [(tf.clip_by_norm(i[0], self.config.clip_val), i[1]) for i in gradient]
self.train_op = optimizer.apply_gradients(clip_grad)
self.grad_norm = tf.global_norm([i[0] for i in clip_grad])
pass
##############################################################
######################## END YOUR CODE #######################
그냥 Linear class 전부 올리겠습니다. 어차피 저거 처음부터 끝까지 다 짜야되는거라;
파이썬 사용법에 그렇게 익숙치 않고, 텐서플로우를 잘 사용하지 않다 보니까 이것저것 다 찾아보며 하느라 힘들었네요.
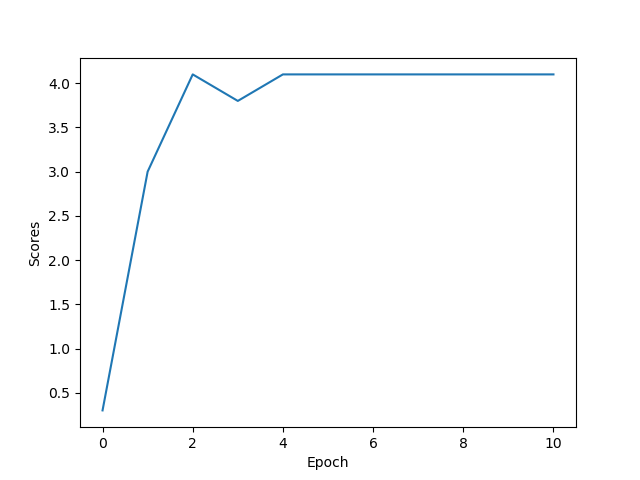
4. test environment에서 얻을 수 있는 최적의 reward를 얻었는가? results/q2 linear에 있는 scores.png 파일을 첨부하여라. [5점]
sol...?) section 1에서 봤던 최적의 reward 4.1이 나오는 모습이다.
앞으로 얼마 안남았다.. 달려봅시다!
'인공지능 > CS234 Assignments' 카테고리의 다른 글
| CS234 Assignment 2-4 solution 및 풀이 (0) | 2019.06.07 |
|---|---|
| CS234 Assignment 2-2 solution 및 풀이 (0) | 2019.06.07 |
| CS234 Assignment 2-1 solution 및 풀이 (0) | 2019.05.29 |
| CS234 Assignment 1-4 solution 및 풀이 (코드) (0) | 2019.05.29 |
| CS234 Assignments 1-2 Solution 및 풀이 (0) | 2019.05.28 |